How AI is transforming the software industry
AI is helping SaaS companies deepen their value proposition
In my earlier post on the history and evolution of AI, I described the shift from traditional software to AI as a pivotal technological shift. I believe that almost all software will eventually have to be AI-powered or AI-led because the gains of embedding AI are phenomenal. SaaS (Software as a Service) companies that lag on this front risk losing share and paving the way for new entrants (likely native AI start-ups) to enter the market.
Over the last few weeks, I’ve been reading about how SaaS businesses are approaching and adopting AI. Panintelligence conducted a survey that highlighted some interesting statistics on the matter:
76% of SaaS firms are either actively utilizing or exploring AI as part of their operations.
38% of SaaS companies have introduced Generative AI features within the past year; another 15% are in the experimental phase
43% of SaaS companies are using machine learning
These numbers show growing interest in and accelerating adoption of AI among SaaS businesses. My recent explorations into how prominent SaaS businesses are integrating AI have been revealing, particularly in understanding how and where it adds value. Below are some short case studies that bring this to life:
1. Supercharging creativity (Adobe)
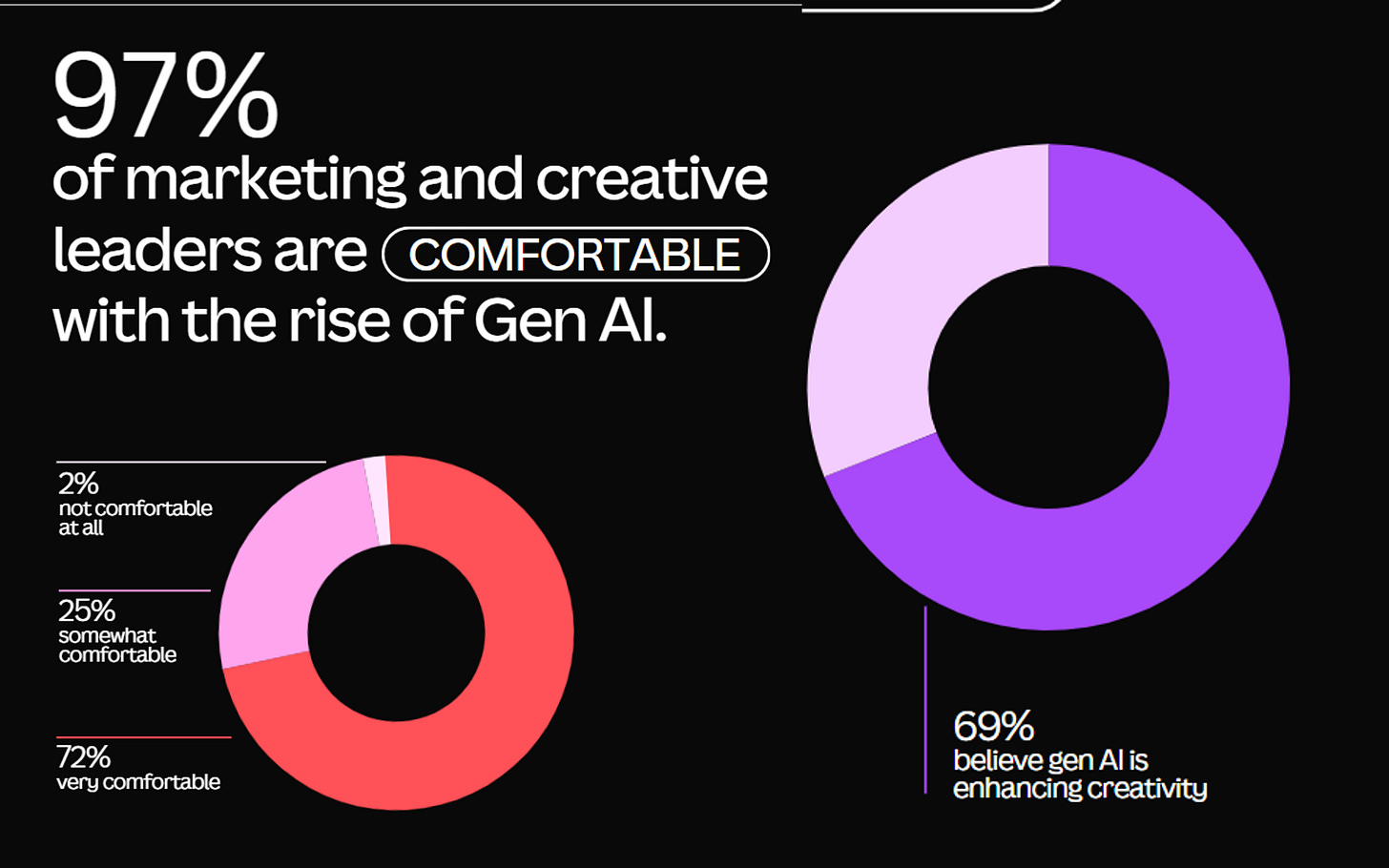
AI is powering creative work by not only delegating repetitive tasks to bots but also improving end-to-end workflows involved in content creation, whether writing, graphic, or video design. Generative AI has been especially transformative by providing everyone’s imagination an outlet. Canva’s AI and marketing report, which surveyed over 4,000 global leaders highlighted that 72% of marketing and creative leaders are comfortable with the rise of Generative AI and 69% believe that it enhances creativity.
Adobe exemplifies a company whose value proposition is greatly enriched by AI. Last year, Adobe introduced FireFly, a suite of creative generative AI models integrated across Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Express, and Adobe Experience Cloud. FireFly enables creators to generate images from simple text prompts, facilitating the creation of new graphics, unlocking novel color combinations, and adding or modifying elements with ease. To date, more than 7 billion images have been created using FireFly.
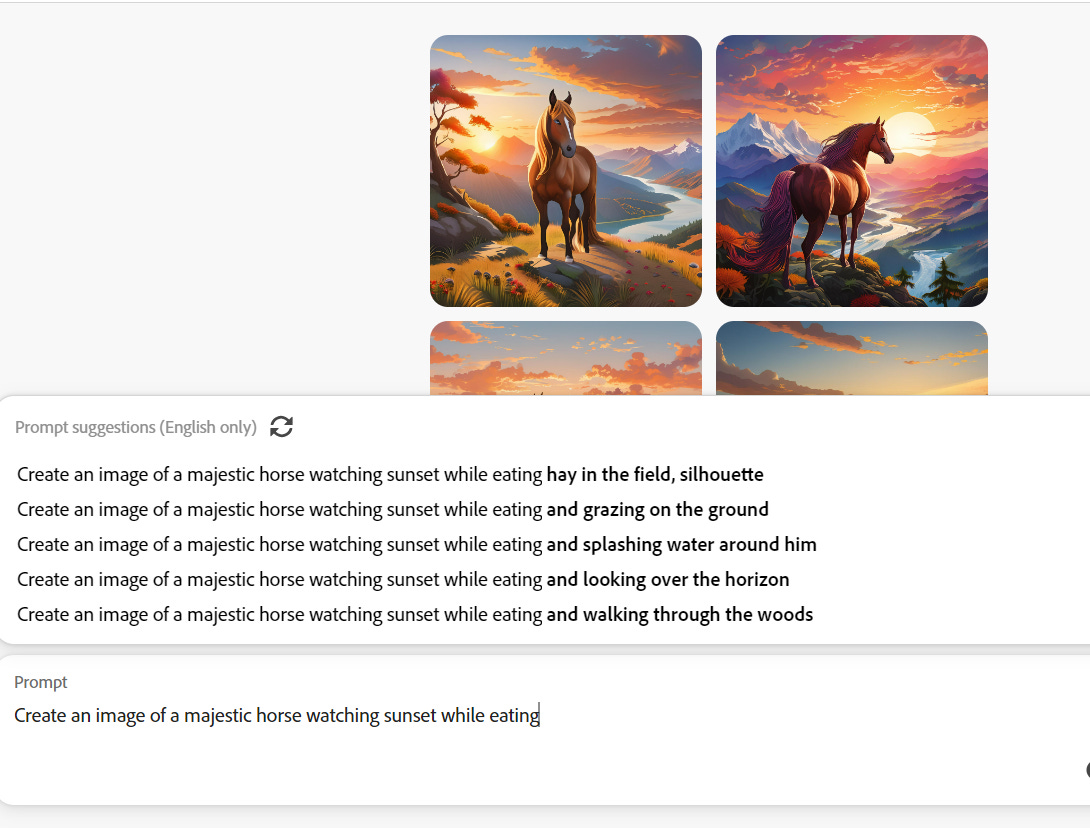
I recently tried the free version of Adobe Express, using the prompt:
‘Create an image of a majestic horse watching sunset’
As someone with limited artistic skills, I value how AI's prompt suggestions simplify the conceptualization process. This is the essence of generative AI: it empowers you to bring your imagination to life effortlessly, without needing to master complex composition rules or design jargon—just by using everyday language.
Boosting productivity through Co-Pilots (Salesforce Einstein & Gong)
Many AI-powered tools are enhancing productivity and efficiency through Co-pilots or assistants. In sales and marketing, the impact of these tools is increasingly evident. According to this Forbes article, sales representatives spend only 35% of their time selling. An average salesperson spends 15% of their time on admin tasks and another 12% on research - areas ripe for automation. Unsurprisingly, only 53% of sales reps hit their sales quota.
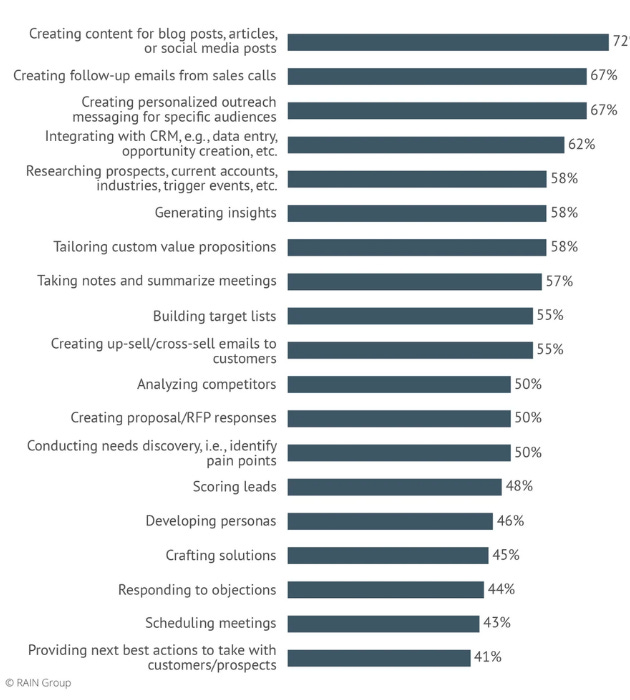
A recent survey by Rain Group, a leading global sales training and consulting firm, reveals that sales teams are increasingly benefiting from AI in a multitude of tasks, as illustrated in the below graphic:
Salesforce and Gong are prominent SaaS companies sales and marketing that utilize AI to automate routine tasks, thus freeing up time for more meaningful customer interactions. Einstein Copilot, an AI assistant, enables sales professionals to offload tasks such as devising customized closing plans for key opportunities, crafting promotions for new products, summarizing calls, and sending personalized emails.
Gong, branding itself as the essential complement to CRM, harnesses AI to extract vital insights from customer interactions, streamline operations, consolidate customer histories into a unified view, and flag potential deal risks. Since February 2023, Gong reports a 464% surge in the number of emails composed using its Generative AI. Additionally, it reports that sales teams guided by AI have seen a 35% increase in win rates.
Improve customer service (Hubspot)
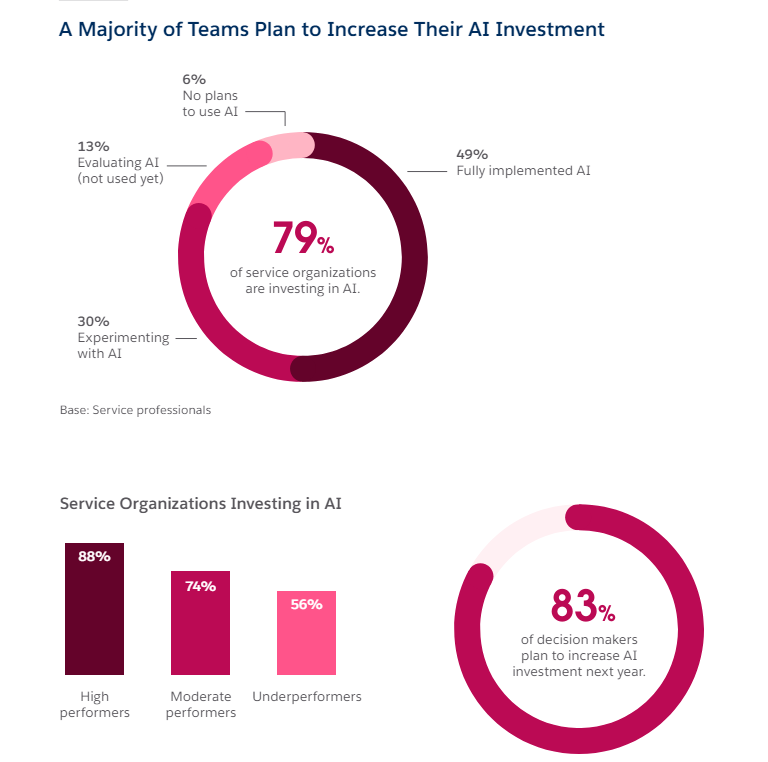
According to Salesforce’s sixth edition of the State of Service report, 79% of service organizations are investing in AI and 83% of decision-makers plan to increase AI investment next year. One of the biggest reasons driving these investments is more time with customers. Userlike conducted a survey in 2022 that highlighted that 68% of users enjoy the speed at which chatbots answer. Software companies are increasingly using AI to improve customer support workflows, reduce response and handle times, and better predict customer behavior.
HubSpot is using AI for augmented messaging, sentiment analyses, request routing and prioritization, voice analyses, and multi-lingual support, among other use cases. Its Service Hub is AI-first, omni-channel, and connected to marketing and sales data on a unified customer platform. It also provides smart support side kicks or AI Assistants to service reps that provide call and conversation summaries and reply recommendations. AI integrations are substantially simplifying the workflow for customer service reps, allowing them to focus on what truly matters.
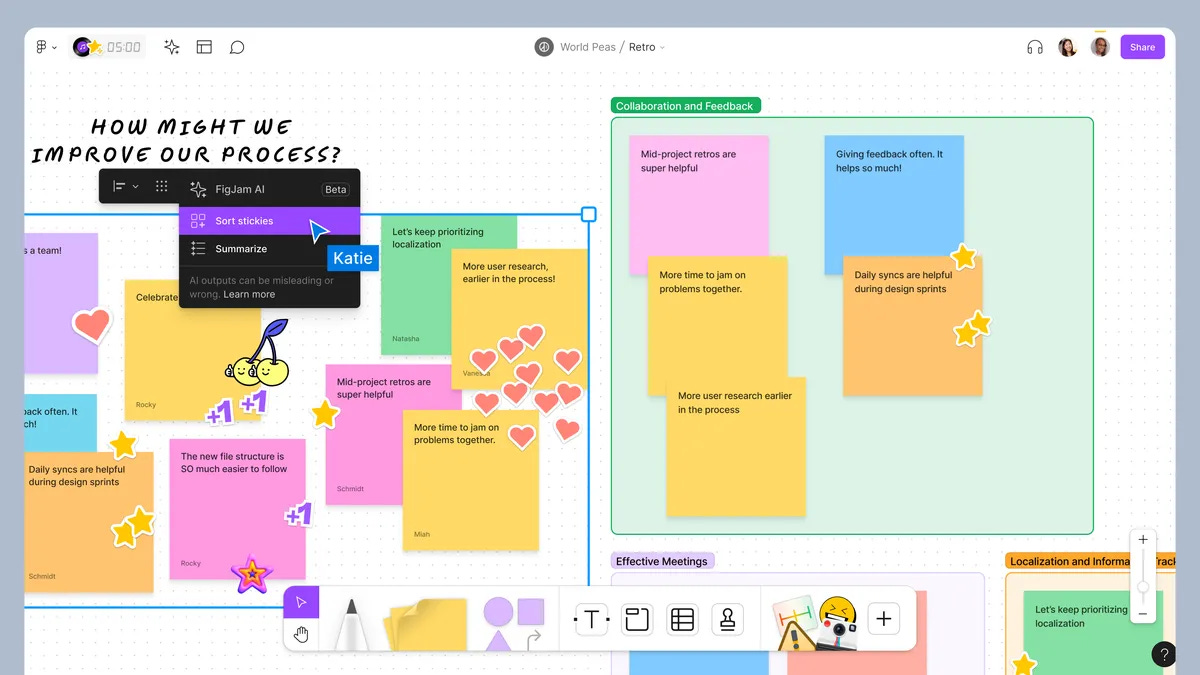
Streamlining workflows (Figma)
Design collaboration platform Figma is leveraging AI to enhance workflows and boost creative processes. Last year, it launched FigJam AI—a suite of generative AI tools within its collaborative whiteboard service, FigJam. These tools provide ready-to-use templates for various design and planning projects. FigJam AI introduces prompt-based assistance, automated diagram generation, content summarization, and dynamic visual feedback. For instance, the 'Sort' function automatically organizes stickies into themed groups, bringing order to a chaotic whiteboard and the 'Summarize' feature compiles information from grouped stickies into a concise summary with just one click. These innovations complement the capabilities of Jambot, a ChatGPT-powered FigJam widget that Figma introduced in beta last August. In an interview with The Verge, Figma Co-founder and CEO Dylan Field said:
“For FigJam I think we’ve been really strategic. Across the entire Figma platform, we’ve thought about all the ways that AI can be useful and narrowed it down to a few use cases where we can bake it into the product in a deep way that really helps”
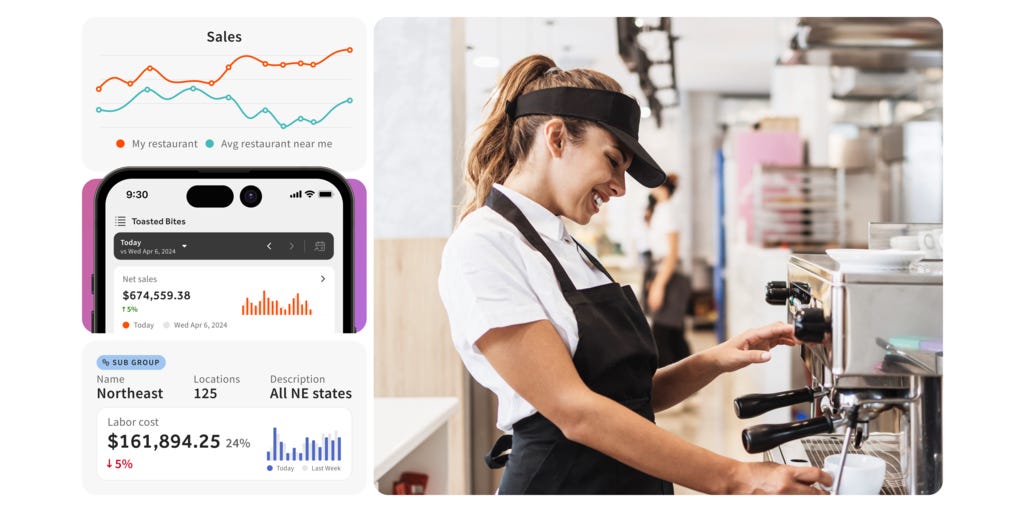
Making better decisions (Toast)
AI can enhance decision-making through predictive analytics by enabling organizations to forecast future trends and behaviors with high accuracy. Toast, a cloud-based platform for restaurants is leveraging AI in its new Restaurant Management Suite. According to a recent survey by Toast, the top challenges for operators include the administrative aspects of the restaurant business, including managing multiple service channels and locations and interpreting guest data. By analyzing data from over 100,000 restaurant locations, Toast's suite provides actionable insights that help restaurant owners and managers make informed decisions about menu changes, pricing strategies, and operational improvements.
The suite's advanced analytics tools utilize AI to perform competitive benchmarking and sales forecasting, offering tailored recommendations that drive efficiency and growth across multiple locations. This application of AI both streamlines the decision-making processes and fosters a more proactive management approach, crucial for staying competitive in the dynamic restaurant industry.
Strengthening cybersecurity
AI in cybersecurity is a double-edged sword as while it can be used for good by defenders to prevent cyberattacks, it can also be used by bad actors to launch more sophisticated and effective attacks. A survey by the Economist Intelligence Unit revealed that 49% of global executives and security experts consider AI & ML as potent tools to combat modern cyber security threats.
I recently attended a session at the AIAI Summit by Lee Klarich, CPO of Palo Alto Networks. One thing he highlighted that stuck with me was how much worse the 2020 Solarwinds attack could have been if it was AI-led. For context, SolarWinds is a Texas-based network monitoring software whose source code was infiltrated by a group believed to be backed by the Russian state. The attacker went through systematically starting with US government organizations, then system integrators, then cybersecurity companies, and ended up getting through to about 100 targets. Their analyses revealed that the attackers could have reached 3000 if they weren’t constrained by resources. Now, if the hackers weren’t relying on people but instead on bots, they could have run a much larger operation targeting all 3000 in parallel. To counter such sophisticated large-scale AI-led cybersecurity attacks, enterprises will need advanced AI-based protection measures.
He mentioned that AI can help block zero-day attacks by processing millions and potentially billions of unique events that have never been seen before such as new files, websites, or DNS connections. By stitching together data via data models and running AI detection capabilities against stitched data, they can better detect and respond to attacks in real-time. With AI, MTTR (Mean Time To Remediation) can go down from days to hours to minutes. This approach not only substantially limits the damage but also dramatically reduces the workload on human security teams.
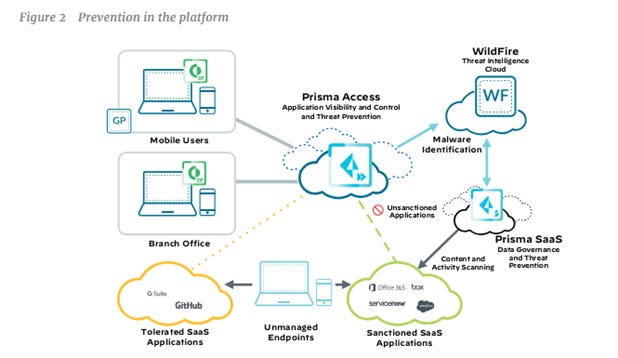
This is particularly important for SaaS platforms, which deal with diverse requirements and configurations, and operate in dynamic environments with continuous updates and integrations. These platforms often store vast amounts of data on centralized cloud servers and share infrastructure among multiple tenants, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. The following diagram, sourced from Palo Alto Network’s AI&ML SOC report, displays a cybersecurity framework where mobile and branch office users interact with various SaaS applications and highlights how differentiated handling of sanctioned, unsanctioned, and tolerated applications ensures comprehensive security.
Concluding Thoughts
Many other SaaS companies like Notion, Box, Ironclad, Slack, Zoom, Docusign, Zendesk, Autodesk, and Dropbox among others are integrating AI into their product to deepen their proposition. I believe that the growing adoption of AI within SaaS platforms represents more than a trend; it represents a critical evolutionary step in today's digital ecosystem. From enhancing creativity and productivity to improving customer service and streamlining workflows, AI is proving indispensable. Moreover, as the cybersecurity challenges mount, the strategic deployment of AI is crucial for both enhancing security measures and ensuring rapid response capabilities to maintain business continuity.
As AI technology continues to advance, its adoption will increasingly become a cornerstone for success and survival in the highly competitive SaaS market. Of course, 'AI-washing' or simply paying lip service to AI won't cut it—true integration to add real value to users will be the way forward in creating lasting value and competitive advantage.